Introduction
Thermal transfer printing technology is essential in many industries due to its ability to print information quickly, efficiently, and economically. In this guide, Comercial Arqué explores the process, applications, types of ribbons, and advantages of this technology, as well as environmental considerations and future trends.
1. What is Thermal Transfer Printing?
Definition
Thermal transfer printing is a digital printing method in which heat is used to transfer ink from a coated film (known as thermal transfer ribbon, ribbon, or TTR) to a substrate, which is mostly paper, synthetic materials, and textile supports. This technology is preferred for its ability to create durable and resistant prints under various environmental conditions quickly and easily.
History
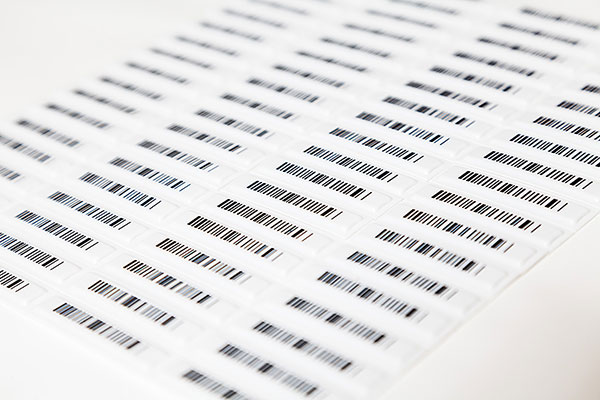
The first patent mentioning Thermal Transfer Ribbon was registered in Japan in 1982 by the company Dai Nippon Printing Co. Subsequently, patents were also registered in the USA, Germany, and China, introducing improvements over the years. In terms of printers, IBM launched the first printer using ribbon in the 1980s. Since then, thermal transfer printing has evolved significantly, becoming a key technology for printing labels with the necessary information for the consumer, especially in the printing of barcodes, texts, QR codes, batch numbers, expiration dates, and a wide variety of applications.
Differences from Direct Thermal Printing
Unlike direct thermal printing, which applies heat directly to a heat-sensitive substrate (usually paper), TTR thermal printing uses a very thin PET (Polyester) film coated with a solidified ink that melts when in contact with a thermal print head. This allows only the desired image to be transferred and firmly anchored to the substrate in a clear and durable manner.
2. Thermal Transfer Printing Process
Main Components
- Print head: Heats specific elements through heat points that define the resolution (the higher the number of heat terminals, the higher the resolution) and transfer the ink to the medium to be printed.
- Thermal transfer ribbon: Contains the ink that is transferred to the substrate.
- Substrate: The material on which printing is done, which can be paper, polyester, polypropylene, among others.
Process Steps
- Data reception: The printer receives data from software installed on a computer or another input source.
- Print head heating: The elements of the print head heat up according to the desired image or text.
- Ink transfer: The heat melts the ink on the ribbon, transferring it to the substrate.
- Ink adherence: The ink permanently adheres to the substrate as it cools down.
Critical Parameters for Print Quality
- Temperature control: Adjusting the print head temperature is crucial for proper ink transfer. The temperature setting may require fine adjustments depending on the ribbon and substrate used.
- Printing speed: Speed affects performance. High-speed printing may require additional adjustments to maintain print quality.
- Print darkness: Controls the density of the printed image, important for achieving optimal contrast and readability.
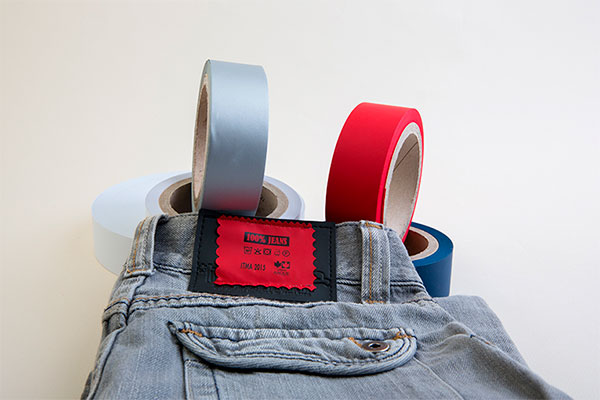
3. Types of Thermal Transfer Ribbons
Wax Ribbons
- Composition: Wax as the main component
- Use: Suitable for applications where durability is not critical.
- Advantages: Economical and easy to use.
- Disadvantages: Less durable, less resistant to abrasion and chemicals.
Wax/Resin Ribbons
- Composition: Mix of waxes and resins of different types depending on the desired effect (resistance, durability, etc.)
- Use: Offer greater durability than wax ribbons, providing good resistance to abrasion and tearing.
- Advantages: Balance between cost and durability.
- Disadvantages: More expensive than wax ribbons, but less durable than resin ones.
Resin Ribbons
- Composition: Contain a higher proportion of resin and are very specific depending on the intended use (resistance to chemicals, temperature, etc.)
- Use: Ideal for extreme environments
- Advantages: Maximum durability and resistance.
- Disadvantages: More expensive and require precise settings to avoid excessive wear on the print head.

4. Common Applications
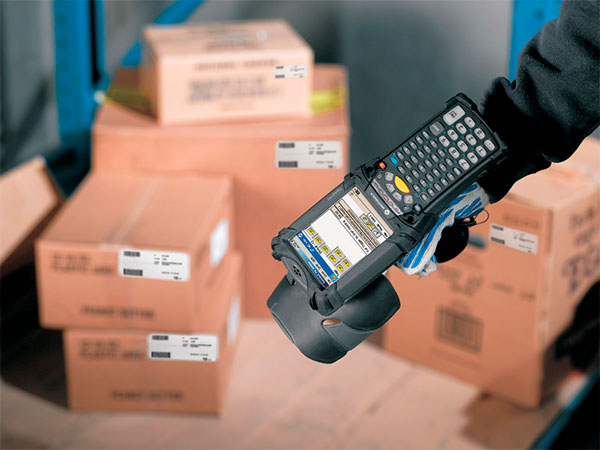
Inventory Management and Logistics
Printing barcodes is crucial for efficient inventory management and logistics, allowing precise and quick tracking of products. Thermal transfer technology ensures that barcodes remain readable and durable over long periods.
Asset Labels
Asset labels help in tracking and managing equipment and other important assets in various industries. These labels must be durable and resistant to adverse conditions, which is achievable with thermal transfer printing technology.
Healthcare Sector
Used for labeling medical records, patient identifiers, and medications, improving safety and efficiency in the healthcare sector. Printed labels must be legible and durable, withstanding constant handling and exposure to chemicals.
Laboratories
Laboratories rely on thermal transfer printing for accurate labeling of test tubes, sample containers, and slides. Durability and resistance to chemicals and environmental conditions are crucial in this context.
Fashion and Accessories
Labels printed with this technology provide detailed information on care, composition, and size of clothing and accessories, enhancing product presentation. High-quality printing is essential for maintaining a good brand image.

5. Advantages of Thermal Transfer Printing
High Print Quality
Capable of producing high-resolution and clear prints, essential for applications where precision and readability are critical, such as barcode scanning. The prints are sharp and detailed, fundamental for industrial and commercial applications.
Durability
Prints are resistant to adverse environmental conditions, including heat, humidity, and chemicals, ensuring a long life for the labels. This is especially important in applications where labels are exposed to rigorous conditions.
Versatility
Can print on a wide variety of materials, allowing its use in multiple industrial applications. The ability to adapt to different substrates makes this technology extremely flexible and useful in various sectors.
Flexibility
Allows customization with variable data such as serial numbers, expiration dates, and batch codes, facilitating tracking and traceability. This flexibility is crucial for applications that require frequent changes in printed information.
6. Environmental Considerations and Future Trends
Sustainability
The thermal transfer printing industry is moving towards more sustainable options, developing eco-friendly ribbon materials and substrates to reduce environmental impact. This includes using ribbons with thinner polyester layers to reduce plastic usage and carbon footprint, as well as recyclable substrates. Additionally, implementing more efficient and sustainable production processes.
Integration with Industry 4.0
Enhanced connectivity allows remote monitoring and management of printers, improving efficiency and traceability in production processes. Integration with Industry 4.0 systems enables more precise control and optimization of printing processes.

Technological Innovations
The continuous development of advanced technologies and improved materials promises to further expand the capabilities of thermal transfer printing. This includes improvements in print resolution, ribbon durability, and energy efficiency of printers.
Conclusion
Thermal transfer printing technology is a robust and versatile solution for a wide range of industrial applications. Its ability to produce high-quality and durable prints makes it a preferred option for many industries. With the ongoing evolution towards more sustainable materials and integration with advanced technologies, thermal transfer printing remains a vital tool in the world of printing and labeling. For more information on our thermal printing and ribbon solutions, visit our website and contact us at Comercial Arqué.